Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
oVirt Serial Console
Summary
Allow direct ssh access to the virtual serial consoles of the VMs managed by an oVirt engine instance, using a SSH proxy server.
Owner
- Name: Francesco Romani (fromani)
- Email: fromani@redhat.com
- Name: Vitor de Lima (Vitordelima)
Detailed Description
Up until oVirt 3.6.0, VMs can be accessed by logging into Engine, using a browser. This feature will allow users to directly connect to the VM’s serial consoles, emulated through virtio channels, using ssh, without directly accessing Engine. Engine will still be used by in background to learn about VM placement, and to store authentication keys.
Benefit to oVirt
The benefit for oVirt is greater flexibility and easier access to VMs for admistrative purposes.
Dependencies / Related Features
Depends on the new ovirt-vmconsole package.
Documentation / External references
ovirt 3.6 deep dive: guest serial console slides and video
Testing
TODO
Contingency Plan
Instructions about how to manually setup the serial console connectivity will be provided below (see section: Manual Configuration) This feature add an independent functionalty, so in the case this is won’t be ready in time, admins can fallback to manual configuration with no other drawbacks.
Release Notes
For information about setup and troubleshooting, see the Administration Guide
== VirtIO serial console ==
Allow the users to connect directly to the emulated serial console of the VMs, using SSH.
Implementation details
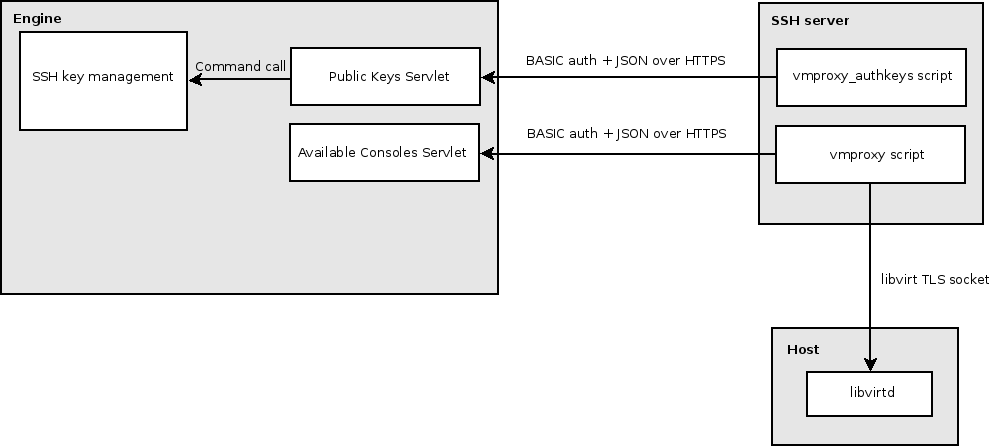
- A secondary instance of the SSH server is used, it allows only one method of authentication (using public keys) and can only login into one user (the vmproxy user)
- The vmproxy_authkeys script lists which public keys are allowed to login and forces a command to be executed after the vmproxy user logs in (the vmproxy command)
- The vmproxy command calls “virsh console” with the appropriate parameters to open a session in the virtual serial console of the chosen VM
- There is a servlet (Public Keys Servlet) inside the engine used by vmproxy_authkeys which lists the public keys and GUIDs of each user
- Another servlet (Available Consoles Servlet) lists the VMs a user is allowed to login and in which host they are located, it is used by the vmproxy script to call virsh console with the appropriate parameters
- The SSH key management creates a public/private SSH key pair, stores the public key in the database with the user record and gives the private key to the user
Detailed Outline
- Access to console will be performed using SSH protocol.
- Proxy based solution, authentication between user and proxy and authentication between proxy and host.
- Separate access to console subsystem using separate unprivileged ssh daemon.
-
Communication between the SSH proxy and the VM console using “virsh console”
User—->[ssh pk(user)]—->SSH Proxy (manager side) —>[TLS socket]—> libvirtd (host side) | V Engine
User Interaction Example
-
Implicit connection, single vm available
$ ssh -i console.key -p 2222 -t vmproxy@engine Fedora release 19 (Schrödinger’s Cat) Kernel 3.13.5-101.fc19.x86_64 on an x86_64 (ttyS0) localhost login:
-
Implicit connection, multiple vm available
$ ssh -i console.key -p 2222 -t ovirt-vmconsole@console-proxy
- vm1 [vmid1]
- vm2 [vmid2]
- vm3 [vmid3]
2 Fedora release 19 (Schrödinger’s Cat) Kernel 3.13.5-101.fc19.x86_64 on an x86_64 (ttyS0) localhost login:
-
Explicit connection:
$ ssh -i console.key -p 2222 -t ovirt-vmconsole@console-proxy vmid3 Fedora release 19 (Schrödinger’s Cat) Kernel 3.13.5-101.fc19.x86_64 on an x86_64 (ttyS0) localhost login:
Known issues
Up until oVirt 3.6.0-rc1, the oVirt Engine configures the console type to “VirtIO”. Unfortunately, this can cause issues with some Guest Operating Systems, and can require additional configuration as well. A Patch is available to switch the default console type “Serial” (Emulated serial console), which should work out of the box in the majority of the Guest OS. The aforementioned patch will be included in oVirt 3.6.0-final.
Note for existing hosts (upgraded from 3.5) the host needs to be re-deployed to correctly install vmconsole packages and set up necessary ssh keys properly. Just rerun the deployment over an existing host.