Feature pages are design documents that developers have created while collaborating on oVirt.
Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
Enable Online Virtual Drive Resize
Summary
This feature allows oVirt users to resize virtual disks while they are in use by one or more virtual machines without the need of pausing, hibernating or rebooting the guests. The virtual disk is disk seen by the guest operating system and should not be confused with the hardware storage (storage domain) which already support online extension.
Owner
- Feature owner: Sean Cohen scohen@redhat.com
- Engine Component owner: Sergey Gotliv
- VDSM Component owner: Federico Simoncelli fsimonce@redhat.com
Current Status
- QEMU
- must support the online resizing of virtual disks: Done in 0.12.1.2-2.295
- Libvirt
- libvirt needs to expose an API to use such capability: Done in 0.10.2-18 (EL) and 1.0.2-1 (Fedora)
- VDSM
- changes to block devices (new SPM API call): Done in v4.12
- additional API call to passthrough to libvirt: Done in v4.12
- oVirt Engine
- need to create a new command to coordinate the entire flow (call to SPM and then call to VM): Done in oVirt Engine 3.3
- oVirt GUI
- need to expose the new functionality: Done in oVirt Engine 3.3
- Rest API
- need to expose the new functionality: Done oVirt Engine 3.3
- QEMU-GA
- support for notifying the guest and updating the size of the visible disk: To be integrated
Limitations
- Shrinking of the virtual drive currently is not supported
- Floating disk, the disk which is not attached to any VM, is not supported
User Experience
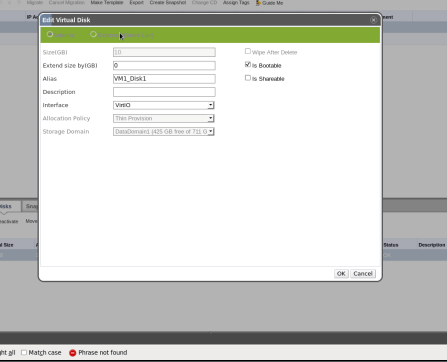
User can extend virtual drive size using UI or REST API.
UI:
- Go to “Virtual Machines” tab and select virtual machine
- Go to “Disks” sub tab and select disk
- Click on “Edit”, pay attention that if disk is locked or VM has other status than “UP”, “PAUSED”, “DOWN” or “SUSPENDED”, editing is not allowed so “Edit” option is grayed out.
- Use “Extend Size By(GB)” field to insert the size in GB which should be added to the existing size
REST API:
Standard updating of virtual machine disk:
PUT /api/vms/{VM_ID}/disks/{DISK_ID} HTTP/1.1
Accept: application/xml
Content-type: application/xml
<disk>
<size>{NEW_SIZE_IN_BYTES}</size>
</disk>
Detailed Description
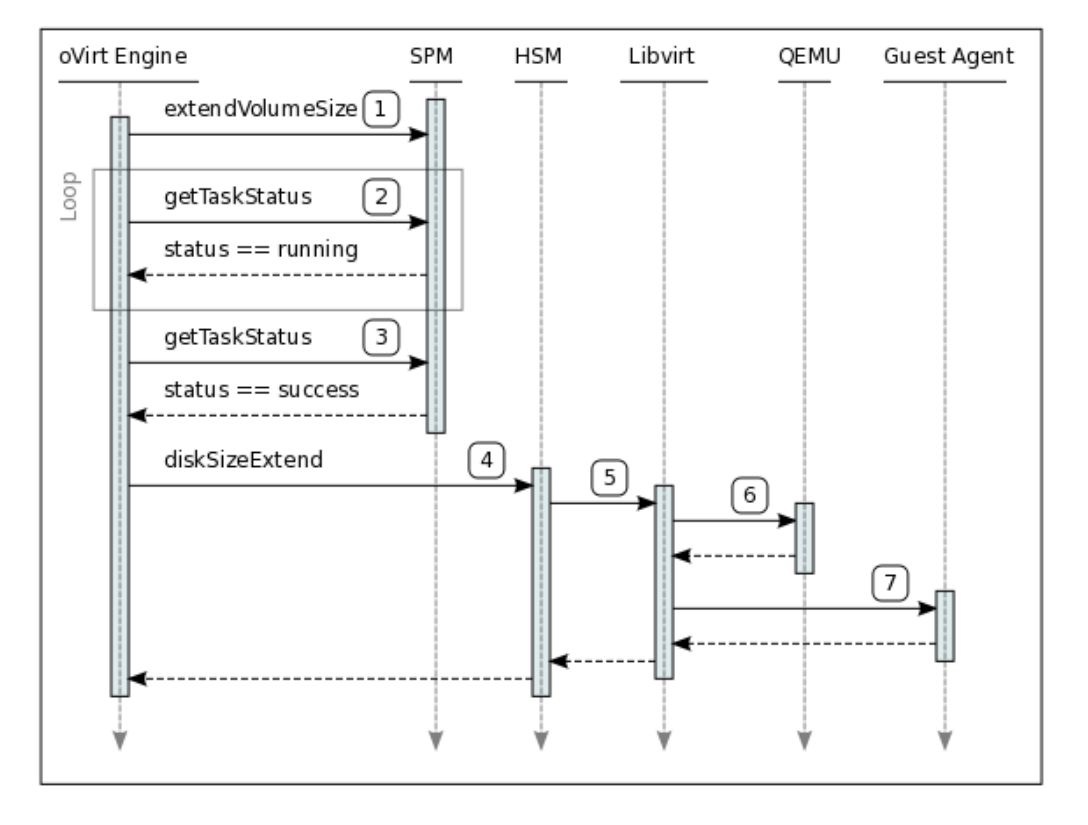
- A request from oVirt Engine is sent to the SPM to extend the image. The scope of this request is mainly to extend the Logical Volume where the image resides and to update the metadata. The extension relevant only when the image is RAW and resides on both a block device and file domain. QCOW images will be treated as a NO-OP at this phase. In the case of a RAW image on a file domain a “truncate” command will be issued on the image to add additional sparse space at the end but we expect the QEMU process to do this anyway as part of its implementation. A preallocated RAW file will be extended using a non-sparse dd command to add zeroes at the end of the image (this is for consistence even if preallocating data on NFS doesn’t guarantee that the space is actually reserved).
- The oVirt Engine polls the
extendVolumeSizestatus. Generally this task is expected to complete quite quickly (NO-OP or lvm command to extend a volume). The only case which might take a long time to complete is preallocating the space on file domains. - The
extendVolumeSizetask is completed with success. - A
diskSizeExtendis sent to the HSM where the virtual machine is running. This command is used to notify the request to extend the image seen by the virtual machine. - The request of extending the virtual image is passed to libvirt as it’s the layered interface on top of the QEMU process (virtual machine)
- The request to extend the virtual image is passed by libvirt to QEMU. QEMU is in charge of truncating the file when relevant, changing the QCOW header of the image (if applicable) to reflect the new size and update all its internal structures (including the ones reporting the disk size to the guest).
- Once the extension is successfully updated on disk (QCOW) and in the internal representation of the QEMU process an optional (in terms of libvirt API) request to the guest agent is delivered to notify the change and to update the guest OS
Documentation / External references
Future Work
- Enable to extend size of the floating disks.