Feature pages are design documents that developers have created while collaborating on oVirt.
Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
Engine High Availability
This page was created as a result of a discussion that started at @engine_devel. As we are considering an active/active architecture for Engine, we’ll use this page to document required features and code changes that will be required.
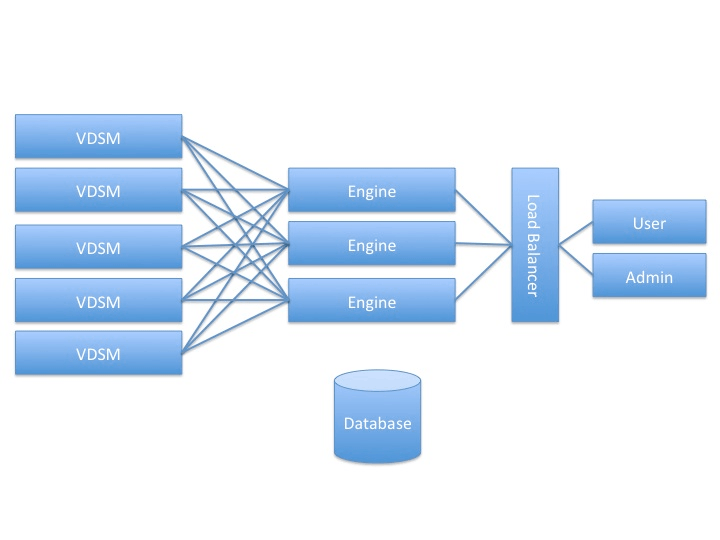
Architecture
Issues with current implementation
- Locking. Currently Engine makes extensive use of Java synchronized capabilities to lock multiple requests hitting the same VDSM at the same time. This should be extended to be cross-machine.
- However, if we replace HTTP transport protocol (and use push notifications), and since VDSM can support multiple concurrent requests, is the entire locking mechanism still necessary?
- Currently there is InMemoryLockManager used by bll commands and monitoring lock in VdsManager. We could find a way to implement InMemoryLockManager to cluster wide using infinispan.
- Singletons. We need to find a mechanism to migrate our singletons to be cross-cluster.
- This is a major issue, since if the Engine running the Singleton crashes, we need to migrate the Singleton. The best solution is to probably dump the Singleton approach. We can ride on the CDI change and the code-refactor it requires.
- Migrating the singletons approach can achieve high availability, but only one active instance running in cluster cannot achieve high scalability which should be a benefit for clustering. To solve this problem, we could:
- Have one instance of the ‘singleton’ running on each node, but make the global variables (should always be maps) in the singleton clustered.
- When the singleton’s methods are invoked, we can:
- use infinispan’s cache listener callback.
- Or we could use infinispan’s distributed execution framework to do the job instead.
- As each singleton is very different, refactoring the code for each specific singleton is probably needed. I’d like to explain details in the Ideas section below.
- EJB. Again as part of CDI change we should drop EJB.
- State clustering. We can use Infinispan, already integrated in Engine, for state replication.
- We will need to consider which state needs to be replicated.
- Quartz. DB configuration for Quartz should enable High Availability.
- Database. DB clustering should be out of scope of this task.
- [Eli] We may consider that as well, please see PostgresSQL HA
- Configuration. All configuration files should be placed in shared storage/database
- VDSM “Sharding”. Should all engines be able to handle all VDSMs, or should we divide VDSMs between running engines (and rebalance once an engine goes down)?
For now I think this is a complex task that we can push for a later stage
Ideas
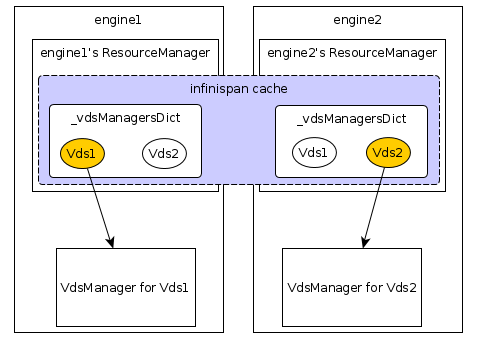
- Clustered singleton approach using infinispan. For example, ResourceManager:
- make global map variable ‘_vdsAndVmsList’ and ‘_asyncRunningVms’ an infinispan cache, both the key and the value are serializable, should be no problem.
- making global map variable ‘_vdsManagersDict’ clustered is not a good idea, because the VdsManager instances should not be passed through network(because it contains connection to vdsm, quartz scheduler…). We could make a owner=1 dist mode cache (which is key-value serializable) to decide which VdsManager instance to run on which engine. So if engine manage multiple hosts, multiple VdsManager instances are distributed to the engine cluster. Here is a overview of the logic: