Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
SR-IOV
Summary
This feature adds SR-IOV support to oVirt management system (which is currently available via a vdsm-hook only).
Owner
- Name: Alona Kaplan (alkaplan)
- Email: alkaplan@redhat.com
Introduction
SR-IOV enables a Single Root Function (for example, a single Ethernet port), to appear as multiple, separate, physical devices. SR-IOV uses two PCI functions:
- Physical Functions (PFs)- Full PCIe device that includes the SR-IOV capabilities.
- Virtual Functions (VFs)- ’lightweight’ PCIe functions that contain the resources necessary for data movement but have a carefully minimized set of configuration resources.
VM’s nic (vNic) can be connected directly to a VF (1-1) instead of to virtual network bridge (vm network). Bypassing the virtual networking devices on the host reduces latency and CPU utilization.
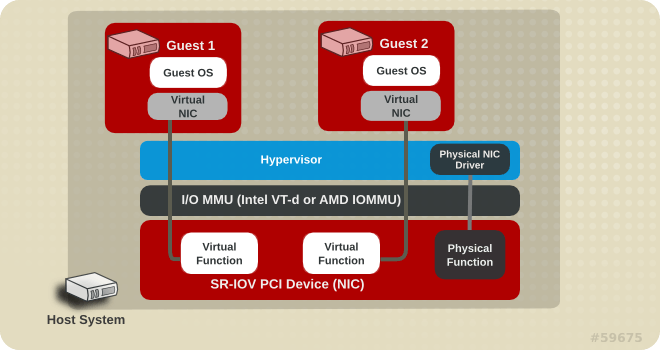
High Level Feature Description
In order to connect a vNic directly to a VF of SR-IOV enabled nic the vNic’s profile should be marked as a “passthrough” one. The properties that should be configured on the VF are taken from the vNic’s profile/network (vlan tag). Each SR-IOV enabled host-nic should have a definition of a set of networks that it is allowed to service. When starting the VM, its vNic will be directly connected to one of the free VFs on the host. But not all PFs are equivalent: the vNic is to be connected via a host-nic that has the vNic’s network as one of its allowed networks.
Note: migration is not supported.
Definitions
- Free VF
- the management system will consider a VF as free if
- the VF is not attached directly to a VM (as reported by
getHostDevListByCaps) - the VF doesn’t have macvatp device on top of it (it is filtered by the vdsm before getVdsCaps, so if the VF is reported by the
getVdsCap, it can be considered it doesn’t have macvtap device on top of it). - the VF doesn’t have network (bridge) or vlan device on top of it.
- notice: although if the VF has any other device (not macvtap, bridge or vlan device) it will be considered as free.
- the VF doesn’t share iommu group with other devices.
- the VF is not attached directly to a VM (as reported by
- the management system will consider a VF as free if
Affected Flows
add/edit profile
- passthrough
- new property that will be added to the profile.
- passthrough property cannot be changed on edit profile if the profile is attached to a vNic.
- port-mirroring is not enabled on passthrough profile.
- QoS is not enabled on passthrough profile.
- the profile cannot be marked as ‘passthrough’ if it has ‘vm network qos’ defined.
add/update network on cluster
- management, display and migration properties are not relevant for the VFs configuration (e.g if a migration network is attached to nic1 via the PF configuration and also exists in the VFs configuration of nic2- the migration will take place on nic1 and NOT on the VF on nic2).
- Same for the required property. It doesn’t relevant for the VFs configuration and related just to the regular network attachments.
add/edit vNic
- if the selected vNic profile is marked as passthrough
- it means that the vNic will bypass the software network virtualization and will be connected directly to the VF.
- vNic type
- pci passthrough
- in case the vnic type is pci passthrough the VF will be detached from the vnic and attached to the vm.
- migration is not supported.
- linking is not supported
- pci passthrough
- the vNic profile/network represents set of properties that will be applied on the VF.
- the vnic profile should be marked as ‘passthrough’
- the compatibility version of the cluster should be 3.6 or more.
hot plug passthrough nic
- plugging
- is possible if there is an available VF.
- the command should update the hostdev table the vf is not free.
- unplugging
- the VF will be released (and free for use).
- the command should update the hostdev table the vf is free.
- available vf - see the definition in runVm.
HostNicVfsConfig
- New entity the will contain all the sr-iov related data on a specific physical nic.
- The data of this entity will be manipulated using-
UpdateHostNicVfsConfigCommand,AddVfsConfigNetworkCommand,RemoveVfsConfigNetworkCommand,AddVfsConfigLabelCommand, andRemoveVfsConfigLabelCommand. - Just nics that support SR-IOV (as reported by
hostdevListByCaps) will haveVfsConfig.
UpdateHostNicVfsConfigCommand
- this command allows editing general SR-IOV related data (vfsConfig) on the nic.
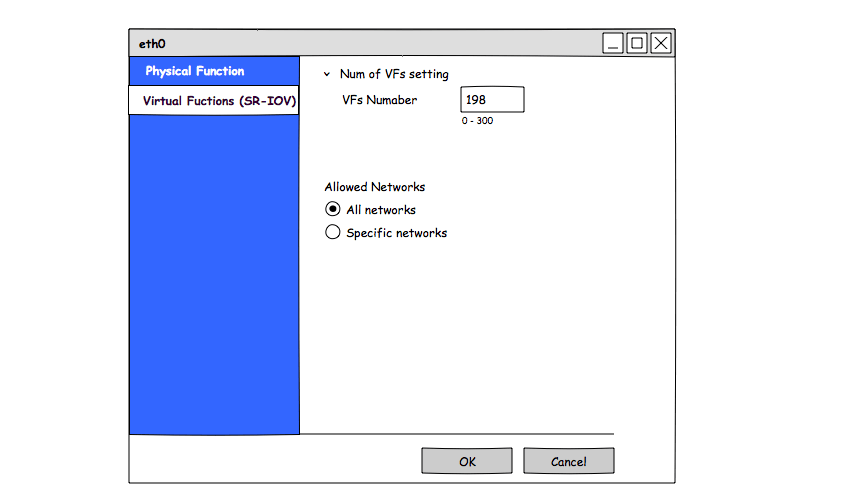
- num of VFs
- num of VFs is a new property that will be added to sr-iov capable host nic.
- it is used for admin to enable this number of VFs on the nic. Changing this value will remove all the VFs from the nic and create new #numOFVfs VFs on the nic.
- valid value is 0 or bigger (up to the maximum supported number by this nic, as reported by
hostdevListByCaps). - this property can be updated just if all the VFs on the PF are free.
- in case ‘num of VFs’ was changed
CollectVdsNetworkDataVDSCommandshould be called.
- all networks allowed
- a boolean property that means there are no network restrictions and all the networks are allowed to be configured on the nic.
- in case ‘all networks allowed’ the network and ‘labels’ lists should be cleared.
- configuring SR-IOV related data on nics that are slaves of a bond is permitted.
AddVfsConfigNetworkCommand
- this command allows adding a network to the vfsConfig network list.
- vfs config network list
- list of the network names that their configuration can be applied on the nic’s VFs.
- it means that if the network of a passthrough vNic is in the list, the vNic can be connected to a free VF on this physical nic.
- the same network can appear in more than one nic’s sr-iov network list.
- list of the network names that their configuration can be applied on the nic’s VFs.
- in case ‘all networks allowed’ is true this command should be blocked.
RemoveVfsConfigNetworkCommand
- this command allows removing a network from the vfsConfig network list.
- for the definition of vfs config network list see
AddVfsConfigNetworkCommand.
AddVfsConfigLabelCommand
- this command allows adding a label to the vfsConfig label list.
- vfs config label list
- a list of labels
- all the networks that their label is in the list will be attached to the sr-iov networks list of the nic (and detached from the network list in case they are attached to it).
- the same sr-iov label can be on more than one nic.
- in case ‘all networks allowed’ is true this command should be blocked.
RemoveVfsConfigLabelCommand
- this command allows removing a label from the vfsConfig label list.
- for the definition of vfs config label list see
AddVfsConfigLabelCommand.
run vm
- scheduling host
- if the VM has a passthrough vNic, the physical nics to which the vNic’s network is attached to are being checked.
- if there are no available VFs on none of the nics, the host is filtered out from the scheduling.
- if all the hosts were filtered out from the scheduling the running of the VM fails and an appropriate error message is displayed.
- if the VM has a passthrough vNic, the physical nics to which the vNic’s network is attached to are being checked.
- the engine will pass the following to the vdsm-
- the VF the vNic should be connected to one of its VFs.
- the network configuration that should be applied on the VF (vlan, mtu).
- should update the hostdev table which vfs are not free anymore.
stop vm
- the command should update the hostdev table which vfs were released (and are free now).
migration
- not supported in case the vm contains a vNic of pci-passthrough type.
parsing the output of hostdevListByCaps
- The following PF info should be determined from the commands output-
- total num of VFs
- reported on the PF.
- num of existing VFs
- counting the number of VFs the PF is their parent.
- num of free VFs
- counting the num of VFs that are marked as free and the PF is their parent.
- total num of VFs
- the command should run-
- on each
CollectVdsNetworkDataVDSCommand - after updateHostNicVfsConfig- in case the number of VFs was updated.
- on each
VDSM API
create
create(Map createInfo)
params = {
(Network VM device struct should be extended)
{
type:hostdev
device:interface
hostdev:vfName
macAddr:<string>
address:{slot=0x02, bus=0x00, domain=0x0000, type=pci, function=0x0}
bootOeder:int
specParams:{vlanid:string}
}
}
- if the vnic type is pci-passthrough
- the VF will be detached from the host and attached to the vm.
- the vnic’s mac address should be applied on the VF before starting the vm.
Virtual functions configuration persistence
- Vdsm will persist the number of virtual functions of a device if a successful call to hostdevChangeNumvfs was made on this device. The persistent information is kept in the file system under /var/lib/vdsm/virtual_functions/ where each file contains a SRIOV device last changed value (/sys/class/net/’device name’/device/sriov_numvfs). An example is a file called /var/lib/vdsm/virtual_functions/0000:02:00.0 which contains “7”. A call for hostdevChangeNumvfs can fail because a software bug, a hardware failure or the failure to listen to the engine client for a certain time period. If a failure has occurred, an attempt to write the last known value will be made.
- During host boot process, Vdsm service will attempt to restore the last persisted number of virtual functions on all managed SRIOV devices before network restoration (assuming some of the persisted networks might be based on SRIOV virtual functions). Failure to do so will fail all network restoration process.
- A SRIOV device that was never configured via hostdevChangeNumvfs will be considered unmanaged by Vdsm and no persist/restore attempts will take place on it.
hotPlugHostDev
not supported in 3.6
hostdevChangeNumvfs
hostdevChangeNumvfs(String deviceName, int numOfVf)
- this verb is implemented as part of hostdev passthrough.
- for sr-iov supported nics this verb updates ‘sriov_numvfs’ file in sysfs (/sys/class/net/’device name’/device/sriov_numvfs) which contains the number of VFs that are enabled on this PF.
- The update is done by first changing the current value to 0 in order to remove all the existing VFs and then changing it to the desired value.
hostdevListByCaps
- hostdevListByCaps-
- SR-IOV related data
- net_iface_name
- PF
- sriov_totalvfs- the maximum number of VFs the device could support
- VF
- iommu_group
- is free
- SR-IOV related data
User Experience
Setup networks
- SR-IOV capable nics
- Should have sr-iov enabled icon

- Edit nic dialog should be expended to contain VFs managenet tab and PF tab
- Edit PF labels
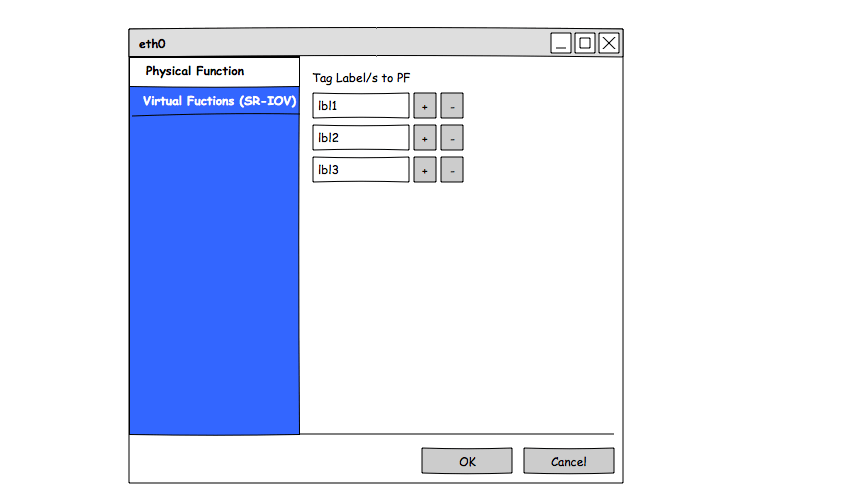
- VFs managenet tab
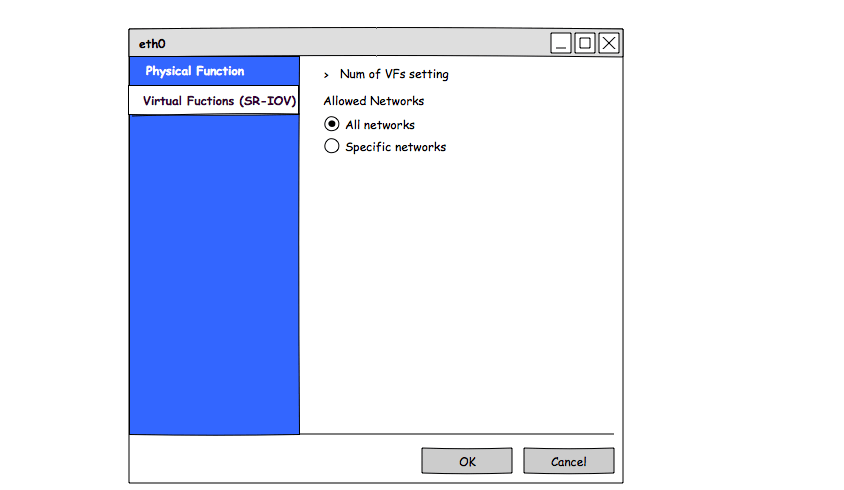
- Edit num of VFs
- Edit VFs networks and labels
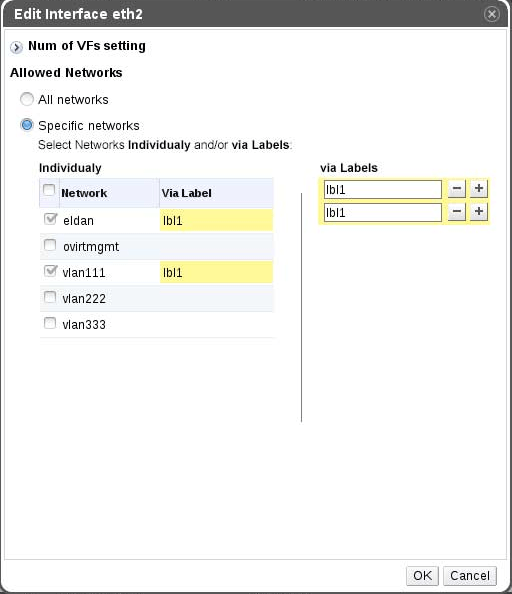
- Edit PF labels
- SR-IOV capable nics which are slaves of a bond should have the same edit dialog as regular SR-IOV capable nics just without the PF tab.
- Nic which don’t support sr-iov shouldn’t have tab at all (should look the same as they look now, before the feature).
- Should have sr-iov enabled icon
Add/Edit vNic profile
- Passthrough property is added to the dialog.
- If passthrough is true, port mirroring and QoS should be disabled.
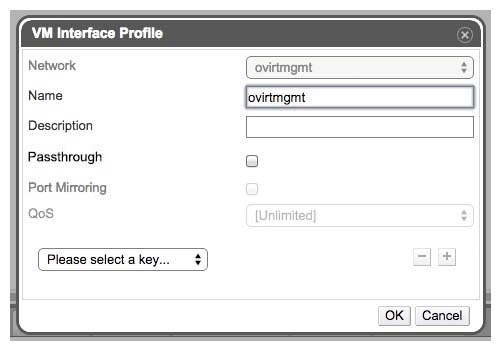
Add/Edit vNic
- Should contain validations- just ‘passthrough’ profile can be attached to vnic profile of ‘pci-passthrough’ type.
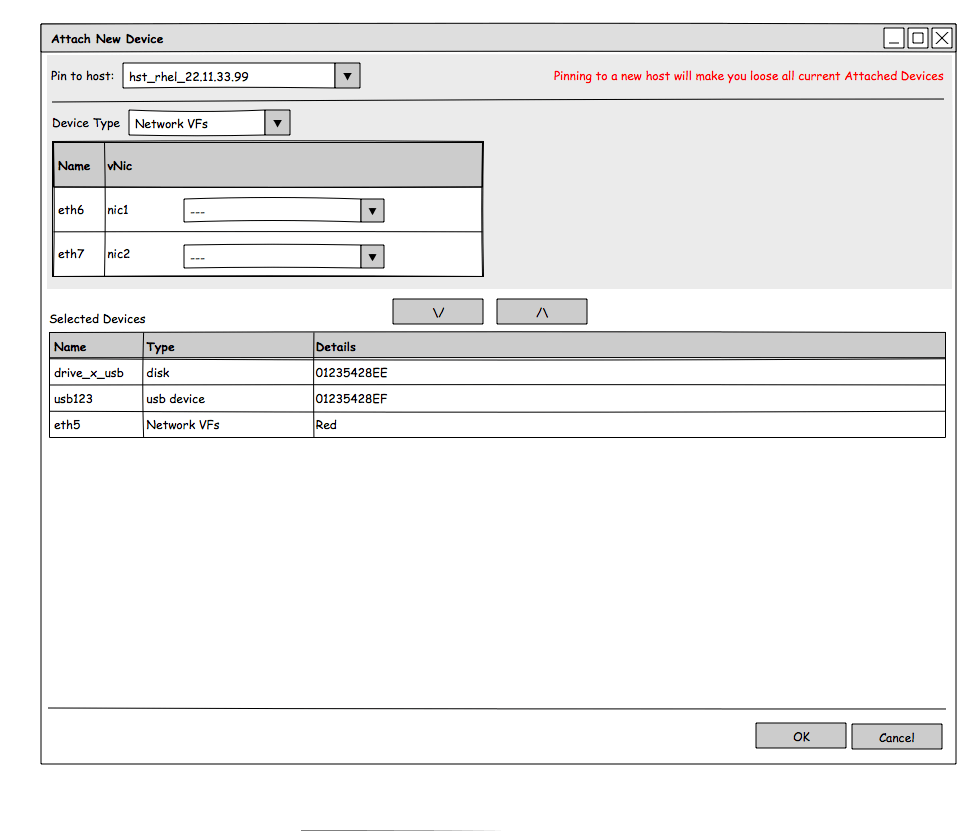
Add host dev device
 ]
]
- This dialog is used in case the user wants to pin a vnic to a specific VF.
REST API
Vnic profile
api/vnicprofiles/[profile_id]
Adding ‘passthrough’ enum property. (this should be enum and not boolean because in the future we would like to add ‘nice to have passthrough’ property without breaking the api).
SR-IOV host nic management
The VFs configuration on a SR-IOV enabled nic is represented as a sub resource of a nic.
/api/hosts/[host_id]/nics/{nic:id}/[vfsConfig:id]
- Supported actions:
- GET return the VFs configuration of the nic (num of VFs, allowed networks and labels).
- PUT updating the VFs configuration of the nic . (executes- UpdateHostNicVfsConfigCommand)
<max_num_of_vfs>max_num</max_num_of_vfs> (read only) <num_of_vfs>num</num_of_vfs> <all_networks_allowed>false</all_networks_allowed>
/api/hosts/[host_id]/nics/{nic:id}/[vfsConfig:id]/networks - Supported actions:
- GET get all the networks configured on HostNicVfsConfig of the specified nic.
- POST adding new network to the list. (executes- AddVfsConfigNetworkCommand)
/api/hosts/[host_id]/nics/{nic:id}/[vfsConfig:id]/networks/<network_id> - Supported actions:
- DELETE removes the network from the network list.(executes-
RemoveVfsConfigNetworkCommand)
/api/hosts/[host_id]/nics/{nic:id}/[vfsConfig:id]/labels - DELETE removes the network from the network list.(executes-
- Supported actions:
- GET get all the labels configured on HostNicVfsConfig of the specified nic.
- POST adding new network to the list. (executes-
AddVfsConfigLabelCommand)
/api/hosts/[host_id]/nics/{nic:id}/[vfsConfig:id]/labels/<label> - Supported actions:
- DELETE removes the label from the network list. (executes-
RemoveVfsConfigLabelCommand)
- DELETE removes the label from the network list. (executes-
Benefit to oVirt
- Configuration of vNics in ‘passthrough’ mode directly from the gui/rest.
- Configuring max-vfs on a sr-iov enabled host nic via setup networks.
Future features
- “Nice to have passthrough”
- Add a property to passthrough vNic profile that indicates whether connecting the vNic directly to VF is mandatory or the vNic can be connected to a regular network bridge in case there are no available VFs on any host.
- A benefit of this “Nice to have passthrough” is that one could set it on vNic profiles that are already used by VMs. Once they are migrated to a new host, the passthrough-ness request would take effect.
- Displaying on passthrough vNic the VF to which it is connected, and the corresponding PF.
- Create a common infrastracture for SR-IOV and VM-FEX.
- Applying on VF the QoS configured on profile/network.
- Support port mirroring on passthrough vNics.
Dependencies / Related Features
- hostdev passthrough
- UCS integration
- PCI: SRIOV control and status via sysfs
- official network adapters support in RHEL
- List of guest operating systems that have available VF drivers for intel nics
- Windows Server 2012*.
- Windows 8*.
- Windows Server 2008 R2*.
- Windows Server 2008*, 32-bit and 64-bit.
- Linux* 2.6.30 kernel or later.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.4* and later.
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.0* and later.
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11* SP1 and later.
Documentation / External references
- BZ 869804: [RFE] [HP RHEV FEAT]: SR-IOV enablement in RHEV
- BZ 984601: [RFE] [HP RHEV 3.4 FEAT]:Containment of error when an SR-IOV device encounters an error and VFs from the device are assigned to one or more guests (RHEV-M component)
- BZ 848202: [RFE] Virtio over macvtap with SRIOV - RHEV Support
- BZ 848200: [RFE] MAC Programming for virtio over macvtap - RHEV support
- 3: oVirt 3.6 SR-IOV deep dive
Open issues
- Duplication of marking the vnic as passthrough. The profile should be marked as passthrough and the vnic type should be “pci-passthrough”
- Advantages
- it makes it easy is to extend the property to- “nice to have passthrough” and “passthrough mandatory” (old scripts won’t break since there is passthrough property on profiles)
- validating that the profile doesn’t contain “qos” and “port-mirroring” is done when creating/editing the profile and not just when getting to the vnic.
- Disadvantages
- Duplication
- Extra validation would be needed to make sure the propties are in sync (vnic with ‘pci-passthough’ type can have just ‘passthrough’ profile attached).
- Advantages
- Is applying MTU on VF supported by libvirt?
- results from the performance team
- compare cpu (macvtap vs tap + bridge vs vf)
- compare team bond w/ passtrhough + virtio vs vf
- migration
- instead of blocking migration in case the vm has pci-passthrough vnics, this marking can be tuned by the admin.
- if the admin requests migration despite the pci-passthrough type, Vdsm can auto-unplug the PCI device before migration, and plug it back on the destination.
- that would allow some kind of migration to guests that are willing to see a PCI device disappear and re-appear.
- instead of blocking migration in case the vm has pci-passthrough vnics, this marking can be tuned by the admin.
- should free/non-free VFs be reported by the vdsm on getVdsCaps?
- today just non-free (with mac or ip) VFs are reported. It is ok we’ll have some kind of regression when stop reporting the VFs at all?
- is it ok we won’t have the possibility to configure regular networks on VFs via setup networks?
- it also means we won’t have the possibility to configure management/display/migration networks on VFs.
- VM QoS
-
- ip link has vlan-qos and tx rate for VFs. Does it really work?
-
- port mirroring (Nir- Should we care about this in the first stage?)
- is it relevant in case of VFs (virtio or pci-passthrough)?
- Does all the VM’s OSs supported by oVirt have driver to support SR-IOV?
Notes
- setting properties on VF
ip link set {DEVICE} vf {NUM} [ mac LLADDR ] [ vlan VLANID [ qos VLAN-QOS ] ] [ rate TXRATE ] [ spoofchk { on | off } ] [ state { auto | enable | disable} ] - Update num of VFs
/sys/class/net/'device name'/device/sriov_totalvfs- contains the num of vfs supported by the device
- just sr-iov supported nics contain this file.
/sys/class/net/'device name'/device/sriov_numvfs- contains num of VFs enabled by the nics.
- In order to update the file the value should first be changed to 0 (i.e all the VFs should first be removed).
- for example
echo '0' > /sys/class/net/eth0/device/sriov_numvfs echo '7' > /sys/class/net/eth0/device/sriov_numvfs
- for example
- read the iommu group of a device
readlink /sys/class/net/<device_name>/device/iommu_group- just sr-iov supported nics contain this file.
- passthrough vnic doesn’t support
- reporting statistics
- mac-spoofing
- port mirroring
- custom mtu
- QoS
- linking
- migration
- run the following command on your host
/sbin/lspci -nn | grep -qE '8086:(340[36].\*rev 13|3405.\*rev (12|13|22))' && echo "Interrupt remapping is broken"if it says the remapping is broken add the
vfio_iommu_type1.allow_unsafe_interrupts=1parameter to the kernel command line-