Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
oVirt LLDP labeler
Summary
oVirt LLDP labeler is a tool that utilizes LLDP support added to oVirt in 4.2. The tool helps to some extent automate network configuration overhead in clusters that are managed by the labeler. It can be used as a separate service or as one-time tool using its cli.
Owner
- Feature Owner: Ales Musil (amusil)
- E-mail: amusil@redhat.com
Benefit to oVirt
The labeler is a service that is capable of helping the oVirt administrator to automate some network related tasks. According to configuration reported via LLDP from peer switch, the labeler is capable of labeling host network interface or bond interfaces together.
Example VLAN flow
Consider following scenario:
Engine contains logical network vlan10 tagged as VLAN with id 10
and label lldp_vlan_10. Multiple hosts that have it’s eth1
connected to switch with VLAN id 10 configured and LLDP reporting
enabled for the interfaces connected to the hosts. To automatically
connect our logical network vlan10 with the eth1 on every host,
the administrator just needs to configure and run the labeler:
First time setup:
1) Write username and password into /etc/ovirt-lldp-labeler/conf.d/ovirt-lldp-credentials.conf
2) Write cluster name and API address into /etc/ovirt-lldp-labeler/conf.d/ovirt-lldp-labeler.conf
Repeatable invocation:
1) Run the oVirt LLDP labeler by executing python /usr/share/ovirt-lldp-labeler/ovirt_lldp_labeler_cli.py
After the labeler run, the hosts will automatically set a lldp_vlan_10
label on top of the eth1 interfaces, which results in the automatic
connection of eth1 with vlan10 network, due to the matching label.
This can be repeated every time a new host is added to the cluster,
as well as for network changes within current hosts e.g. the switch
port connection was switched between eth1 and eth2 on the host.
Prerequisites
The labeler has to be capable of reaching the desired engine REST API and the
python-ovirt-engine-sdk4 in a version greater than 4.2 has to be installed.
Limitations
Currently, only Juniper switches support reporting of the needed parameters. The required parameters are:
Port VLANLink Aggregation
Implementation
Overall architecture:
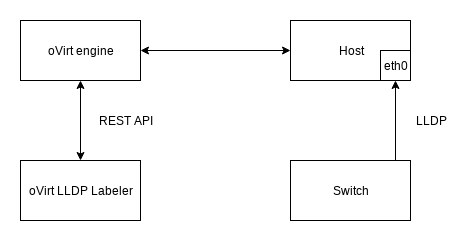
Service
The labeler service is done through timers available in systemd. The timer calls a target which executes the cli tool. The delay is one hour by default and can be changed in the timer specification.
Labeler
The tool itself is divided into two parts. The labeling part and the bonding part, each can be enabled or disabled in the configuration file.
Each step described below is done for each host, that is part of the cluster specified in the configuration file.
-
The bonding part starts by fetching all LLDP available for interfaces that are not part of any existing bond already. The labeler is not trying to modify existing bonds, just to create new ones. The LLDP information is then searched for
Link Aggregationcapabilities. The interfaces, that are capable of aggregation, are grouped together byAggregation Link ID. Before creating a bond, the interface with attachedovirtmgmtnetwork is filtered out, as we don’t want to risk losing connectivity with the host. Also, rules about which networks can be attached to an interface are applied. After creating bond candidates the last step is to re-attach all networks from slaves to the bond candidate. All network configurations made by the labeler are marked as permanent so host restart won’t wipe them. -
The labeling part fetches LLDP from all non-VLAN interfaces and bond slaves. The labeler search every interface LLDP information for
VLAN IDtlvs. For every VLAN tlv, the labeler creates label candidate, in format oflldp_vlan_$(VLAN-ID), where$(VLAN-ID)is substituted with VLAN id from the reported LLDP information. It is possible to have multiple VLAN on the interface, in this case, the interface ends up with multiple labels.
Configuration
The labeler consists of three main configuration files. Full configuration documentation is available in the project readme.
First two files are usually located in /etc/ovirt-lldp-labeler/conf.d/.
The ovirt-lldp-credentials.conf contains login information to access the
engine API. This file is restricted with permission 0600 to prevent any
unwanted access to the file.
usernameusername for Enginepasswordpassword for Engine
The ovirt-lldp-labeler.conf contains basic configuration.
clusterslist of clusters on top of which the labeler will runapi_urlURL of the engine APIca_filepath to certficate that should be used for API accessauto_bondingswitch to enable/disable auto bondingauto_labelingswitch to enable/disable auto labeling
The last configuration file is the configuration of the systemd timer. It is usually
located in /usr/lib/systemd/system/ and it is called
ovirt-lldp-labeler.timer.
OnUnitActiveSecThe timer delay for single labeler runs.
Testing
Run labeler under conditions below:
- Auto bonding disabled
- Auto labeling disabled
- Auto bonding and labeling enabled at the same time
- On top of hosts with VLAN interfaces
- On top of hosts with interfaces, with disabled LLDP reporting
Setup tests:
- Installation
- Security - only the ovirt-lldp-credentials.conf owner should be able to read/write into the config
- Service timer