Most of them are outdated, but provide historical design context.
They are not user documentation and should not be treated as such.
Documentation is available here.
CommandCoordinator Flows and Events
Introduce CommandCoordinator Flows and Events support and internal refactor
Summary
The Command Coordinator was refactored to separate responsibilities of its components and to support command flows and events, based on command-coordinator.
Owner
- Name: Moti Asayag (masayag)
- Name: Liron Aravot (laravot)
- Email: masayag@redhat.com
- Email: laravot@redhat.com
Detailed Description
The existing CoCo implementation provides api for registering a callback to be executed for a command.
However, the api doesn’t define which component is responsible to manage the entire command’s flow. Therefore the callback
is responsible to invoke the next step in the chain, either by managing its own state machine in CommandCallback.doPolling()
or on CommandCallback.onSuccess() or CommandCallback.onFailure().
In addition, there are several mechanism within ovirt-engine to achieve the same result, i.e. SEAT and Command Coordinator. SEAT was a mid-term solution and once Command Coordinator is introduced, it should be deprecated and removed.
Refactor changes
The purpose of the refactor was to separate responsibilities of its components, prevent cyclic dependencies and to easily support adding more metadata which might be required by the commands and their callbacks, i.e. events.
- CommandCallbacksPoller Extracted from previous CommandExecutor class, used to schedule the Quartz job for invoking the callback periodically.
- CommandExecutor is responsible for invoking commands by command-coordinator in the system.
- CommandsRepository is responsible for handling command’s related information, callbacks and caching.
- ConcurrentChildCommandsExecutionCallback implements a callback which should process its child commands in parallel, and continues after all of its child commands executions are completed
- SerialChildCommandsExecutionCallback implements a callback which executes its child commands serially, this callback will terminate the execute if any of the child commands fails.
Support Flows with Command Coordinator
The definition of a flow is determined by the command, by implementing the SerialChildExecutingCommand interface which defines the next operation to perform by:
boolean SerialChildExecutingCommand.performNextOperation()
The command which implements this interface will define the next step of its execution. The action will be triggered by the commands callback (SerialChildExecutingCommand). The invoked actions via performNextOperation() can be either commands, commands with callbacks or tasks or other execution pieces. The orchestration of the flow will be done inside the command, and its progress will be monitored by command coordinator, which upon its child completion will determine if it should be continued or canceled.
The following sequence diagram describes the components and their interaction in executing a command’s flow:

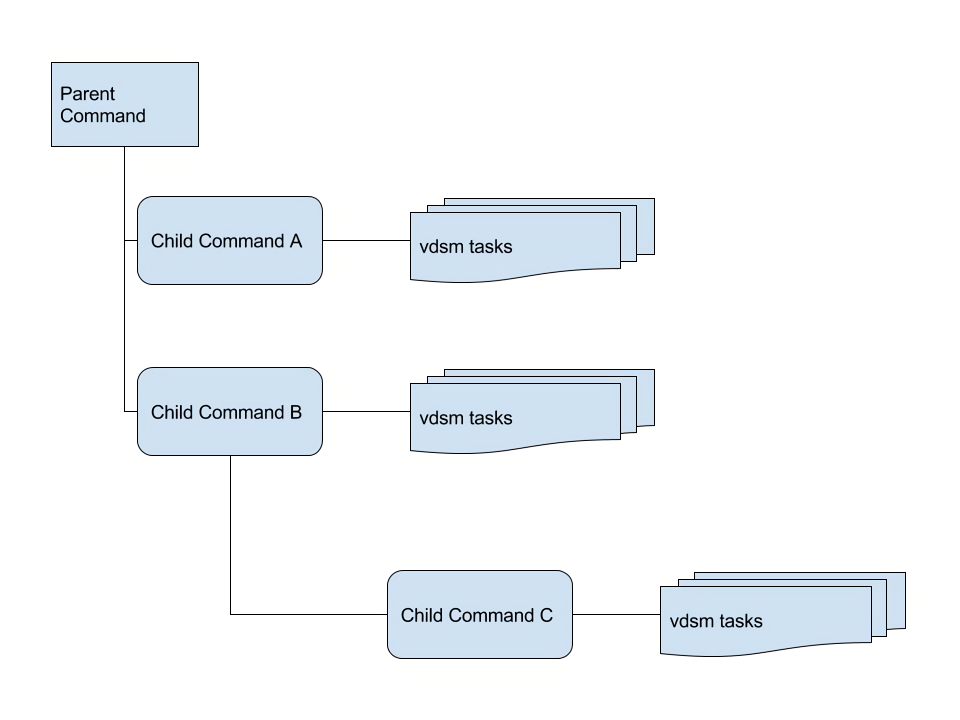
The following diagram describes the supported flows, which might be a combination of a serial and concurrent commands invocation:
Support Events with Command Coordinator
Command should be able to register for an event. The registration is done from the command’s execution block. Registering the command to the event will be done prior to invoking the action which will trigger the event: The subscribed event will be processed asynchronously, hence it would be advisable to register prior to creating the trigger for the event. CommandCoordinatorUtil.subscribe() is the entry point for command-coordinator registration for events. CommandCoordinatorImpl.processEvent() will handle the received the events, and upon arrival of an event, it will invoke the CommandCallback.onEvent().
- Registered callbacks, waiting to be invoked by an event will not be part of the polling
- In case of event not being sent within X minutes, the callback will be moved to polling mode
- After engine server restart, any callback which was wainting for an event, will be moved to polling mode
The event should be identified by a unique-id, i.e.:
Registering for a ‘create disk’ event will be by sending the event-subscriber id: *|storage|create_disk|UUID_of_disk

Benefit to oVirt
With sequential flow, more complex scenarios could be developed. Supporting events in command coordinator is a better alternative for polling the callbacks, as it allows an immediate response for the event which the callback depends on.